Going viral: understanding viral RNA diversity in sharks
The main goals of this project were to:
1. Characterise the RNA diversity in Chondrichthyan hosts and identify a core virome in the group;
2. Assess possible differences in viral RNA communities among major Chondrichtyan lineages: 2 sharks, 2 rays and 2 chimaeras;
3. Compare the viral RNA pathogens of Chondrichtyan hosts with those reported for other aquatic animal taxa: similarities and phylogenetic relationships.
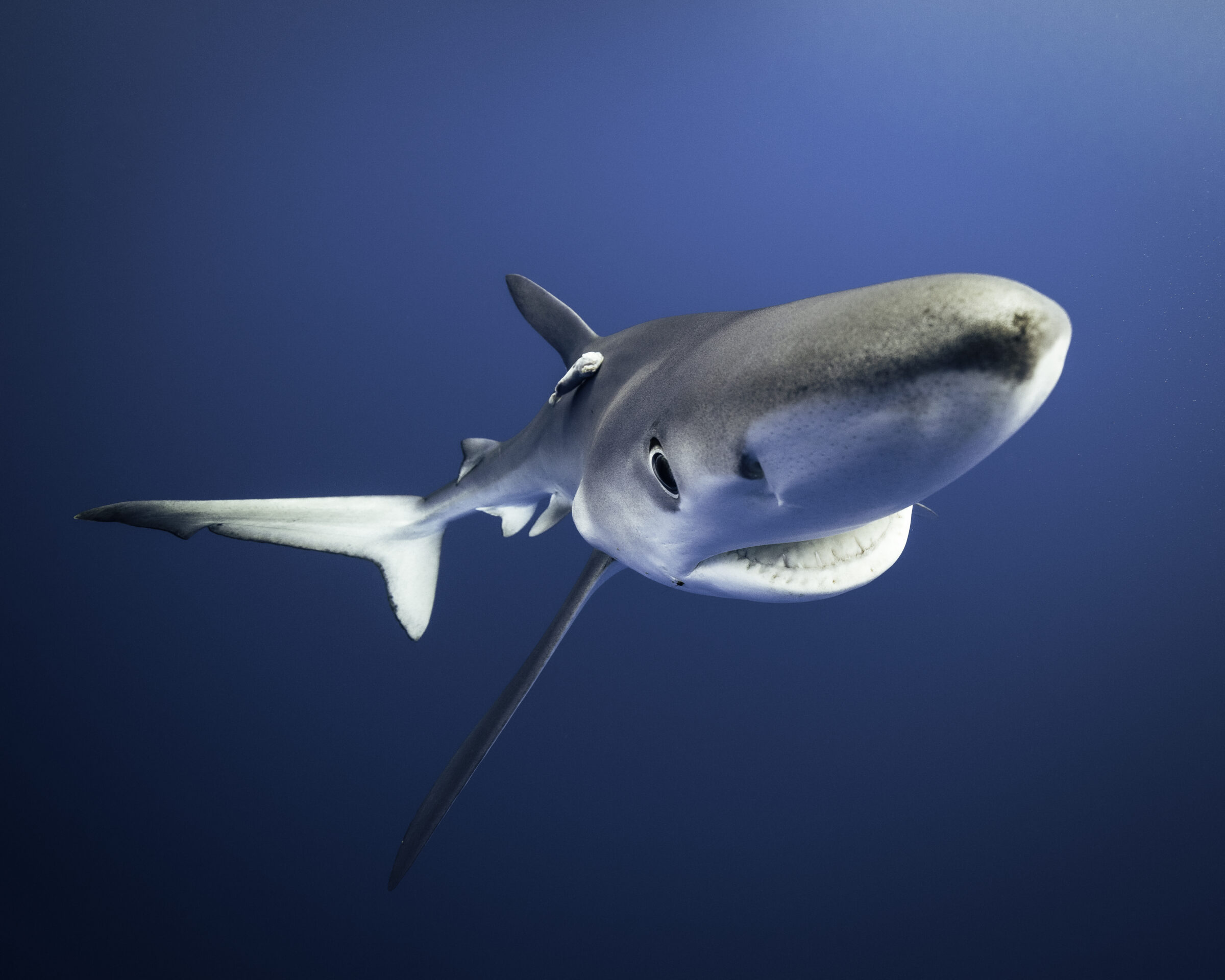

One of the sample species: a blue shark (prionace glauca). Photo © Sebastian Staines | Save Our Seas Foundation
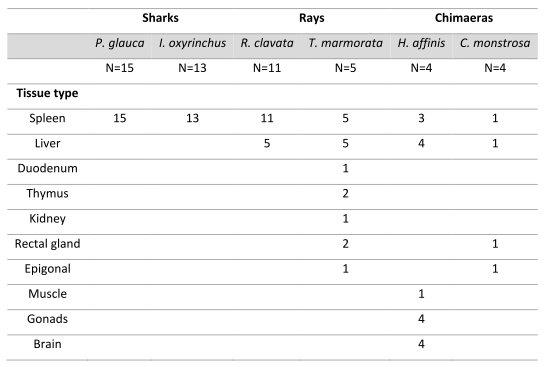
Table showing samples taken for viral RNA extraction. Image © Fabiana Neves
Samples for viral RNA extraction
In total we extracted viral RNA from several tissues and individuals from:
two ocean pelagic sharks
- 15 Prionace glauca individuals
13 Isurus oxyrinchus individuals
- two coastal benthic rays
11 Raja clavata individuals
5 Torpedo marmorata indiviiduals
- two benthic deepwater chimaeras
4 Hydrolagus affinis individuals
4 Chimaera monstrosa individuals.
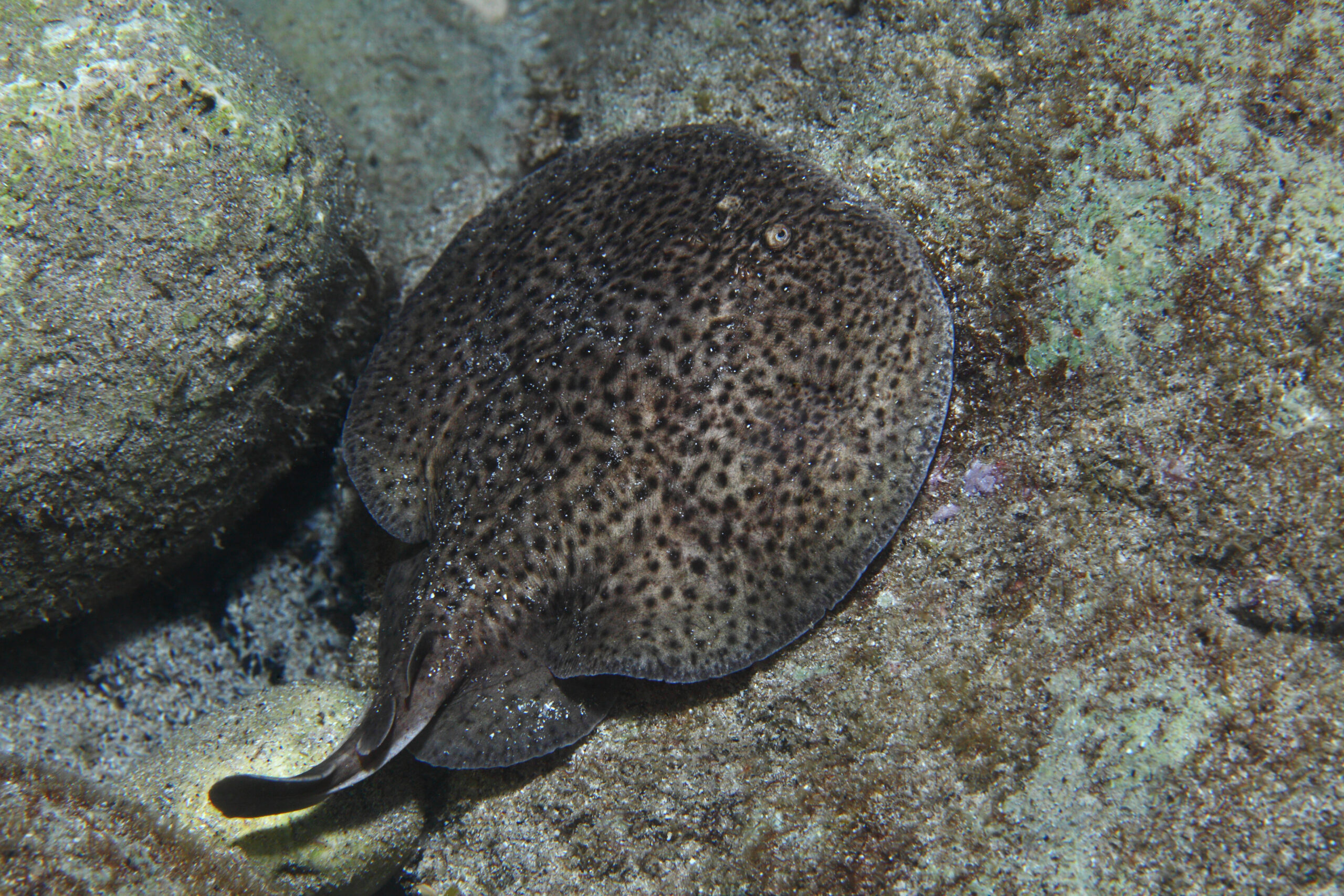

One of the sample species: a marbled electric ray (Torpedo marmorata). Photo © aquapix | Shutterstock
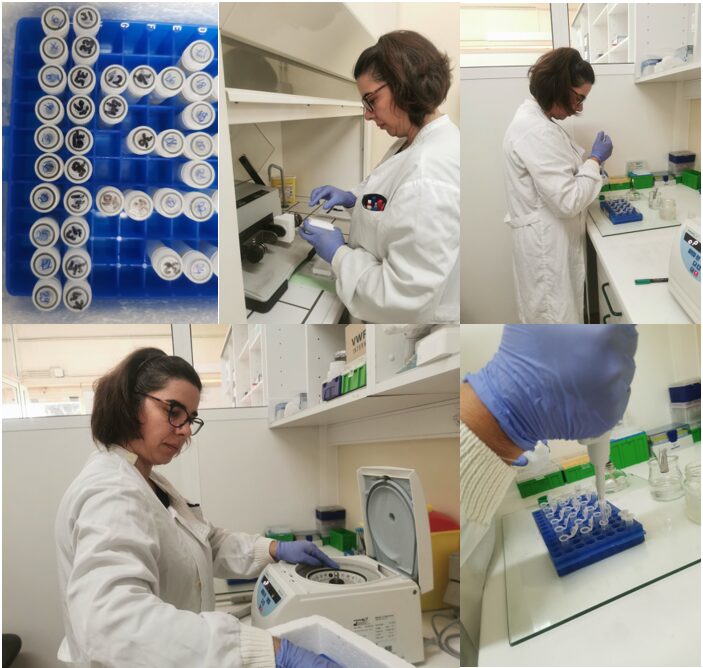

The process of extracting viral RNA. Photos © Fabiana Neves
Methods for viral RNA sequencing and analysis
Samples were pooled by species and sequenced on an Illumina Novaseq6000 at Macrogen
- 150PE libraries
Illumina Truseq stranded total RNA library Prep Kit with host Ribo-depletion
- Bioinformatic pipelineFastQC
Trimmomatic
Bowtie2
Megahit / Spades
Diamond / Blastx
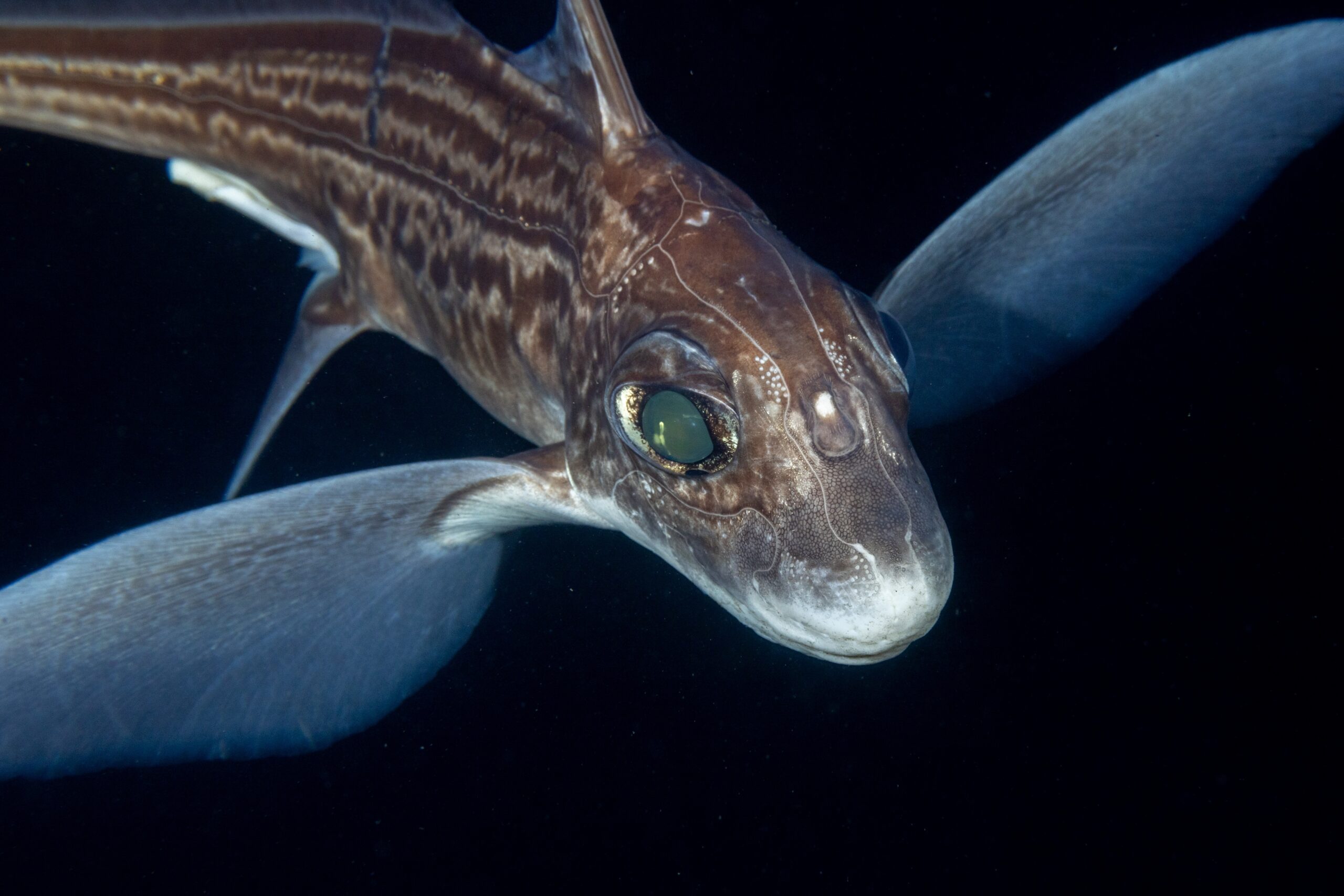

One of the sample species: a ghost shark (Chimaera monstrosa). Photo © Heine Jensen | Shutterstock
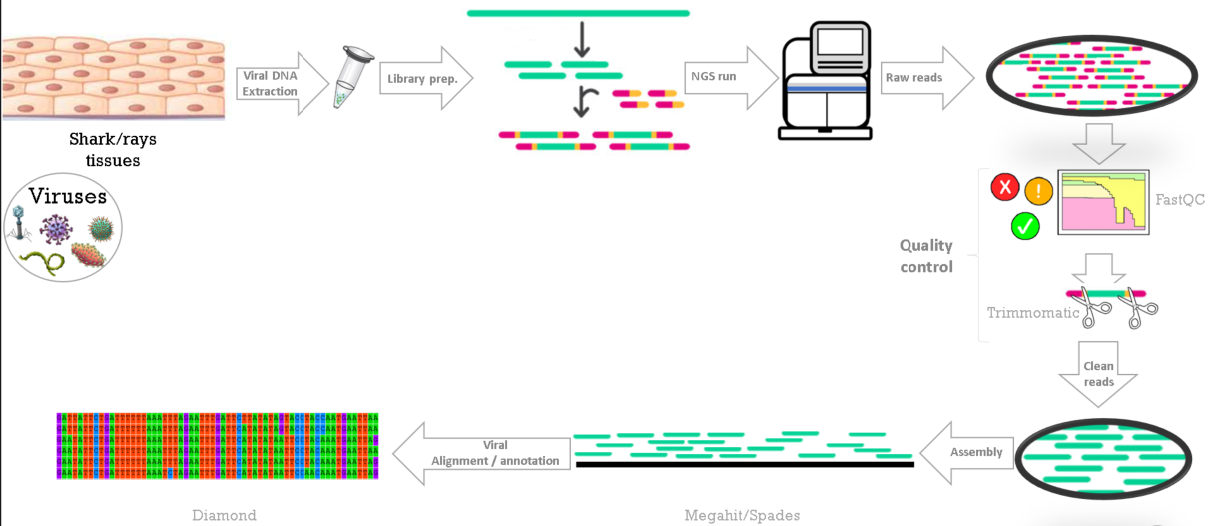
Illustration showing the methods for viral RNA sequencing and analysis. Image © Fabiana Neves
Results / Discussion
Despite the use of internal organs to ensure the detection of viruses, no viral hit was confirmed. This may be due to:
- Type of tissue used?
Maybe in future studies we should focus on swabs (reducing the amounth od host contamination)
- Technical(extraction protocol)/analytical (bioinformatic pipeline) reasons?
other studies sucessfully used same methodology
- Health status of the species?
These individuals were colected during scientific cruisers in their natural environment, and did not presented any signs of disease.
- Viral load amount?
Even if present, if a virus presents a low viral load, may not be sequenced through Next-Generation sequencing.
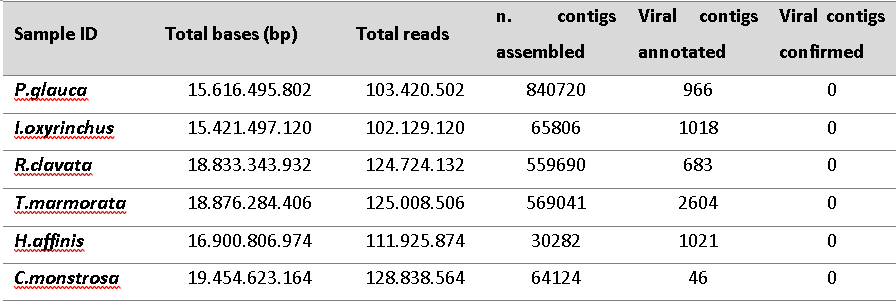
Table showing results of the viral RNA analysis. Image © Fabiana Neves
